Common conditions linked to Intermenstrual Bleeding
Private Medical Consultation
Our doctor will review your menstrual history, contraceptive use, potential pregnancy, current medications, and overall medical background.

Common conditions linked to Intermenstrual Bleeding

Frequent irregular bleeding may indicate hormonal or structural causes.
May suggest infection, cervical changes, or underlying inflammation.
Hormonal fluctuations may require adjustment or review of contraceptive method.
Disrupted cycles may affect ovulation and warrant further investigation.
These conditions often contribute to cycle irregularities or breakthrough bleeding.

Our doctor will review your menstrual history, contraceptive use, potential pregnancy, current medications, and overall medical background.
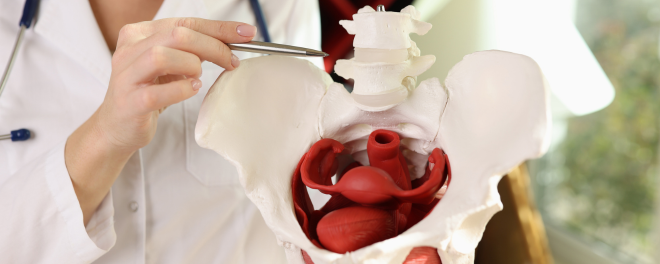
A gentle speculum and bimanual exam will be performed to assess the cervix, vagina, and uterus for visible causes of bleeding.
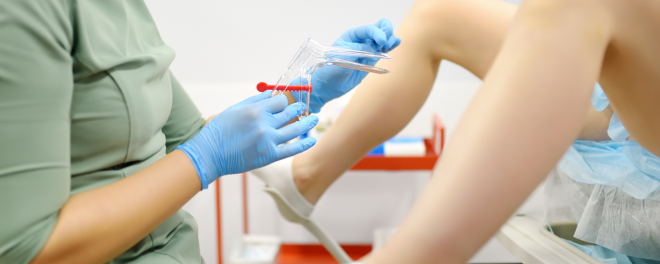
Based on clinical findings, your doctor may recommend:
• Pregnancy test to rule out early or ectopic pregnancy
• Vaginal/cervical swabs to check for infections or STIs
• Pelvic ultrasound to assess for fibroids, polyps, or ovarian cysts
• PAP smear and/or HPV test if cervical screening is due
• Blood tests for hormones, thyroid function, blood count, or other markers

Your treatment may include:
• Hormonal therapy, such as oral contraceptives or progesterone for cycle regulation
• Antibiotics or antifungals for managing infections or pelvic inflammatory disease
• Procedure-based care, such as removal of polyps or targeted fibroid treatment
• Contraceptive method review or change if bleeding is method-related
• Urgent referral, if pregnancy complications (e.g., ectopic pregnancy) are suspected
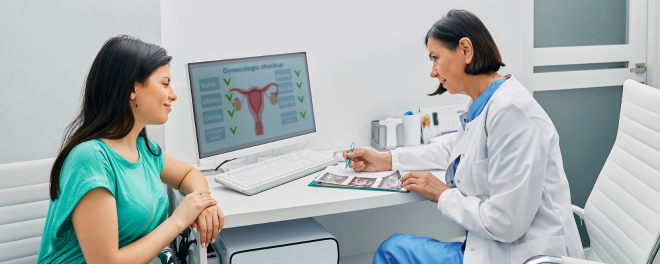
Your doctor will review test results, adjust treatment as needed, and arrange ongoing cycle tracking or preventive screening for continued care.
All intermenstrual bleeding consultations across our medical group are conducted by trained women’s health professionals in a confidential and supportive environment. Care is guided by PHMC guidelines and MOH professional standards, and overseen by doctors registered with the Singapore Medical Council (SMC). Accredited under the SMC APOC framework, our team ensures ethical, safe, and evidence-based care — helping women understand their symptoms and receive tailored management with clarity and reassurance.
Occasional light spotting can be harmless, but repeated or heavy episodes should be assessed.
Yes. Spotting may occur in early pregnancy or with complications (e.g., ectopic). If pregnancy is possible, testing is recommended.
If you’re due—or if your doctor suspects cervical changes—PAP/HPV testing may be advised.
Yes, lifestyle changes can influence hormones and trigger light spotting. Persistent bleeding warrants evaluation.
Breakthrough bleeding is common in the first few months. If it persists, your method or dose may need adjustment.
It depends on the cause. Some cases resolve; others require treatment to prevent complications.
If you have severe pain, heavy bleeding (soaking pads hourly), dizziness/fainting, or positive pregnancy test with pain—seek immediate medical attention.